Laboratory for Drug Design
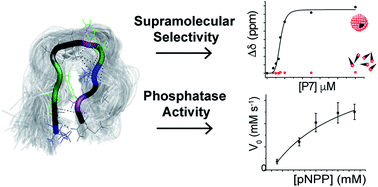
Discovery of phosphotyrosine-binding oligopeptides with supramolecular target selectivity
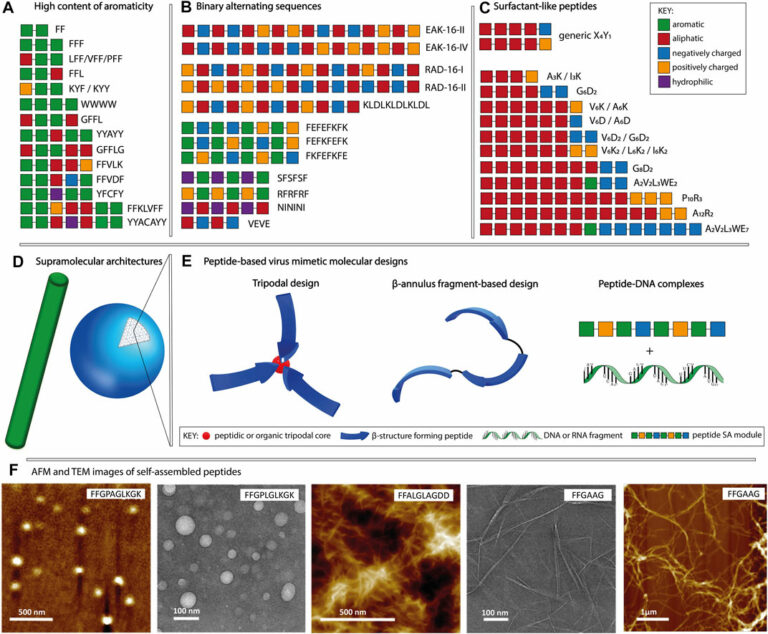
Exploiting Peptide Self-Assembly for the Development of Minimalistic Viral Mimetics
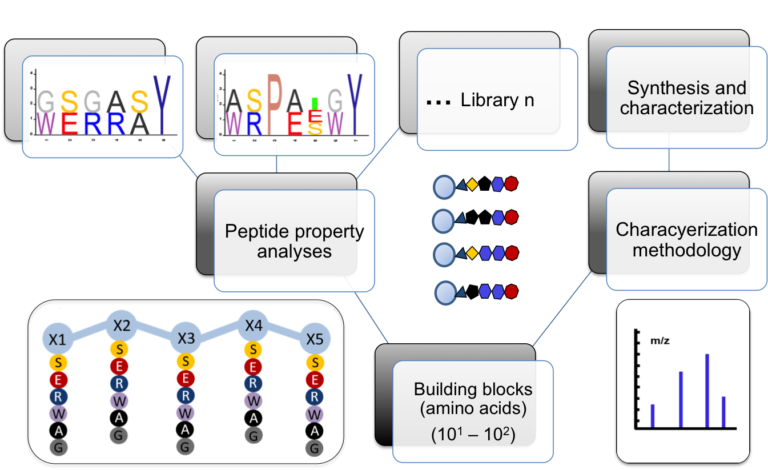
Bottom-Up Design Approach for OBOC Peptide Libraries
Design of short catalytic peptides and peptide assemblies (DeShPet)
Institution: University of Rijeka, Department of Biotechnology
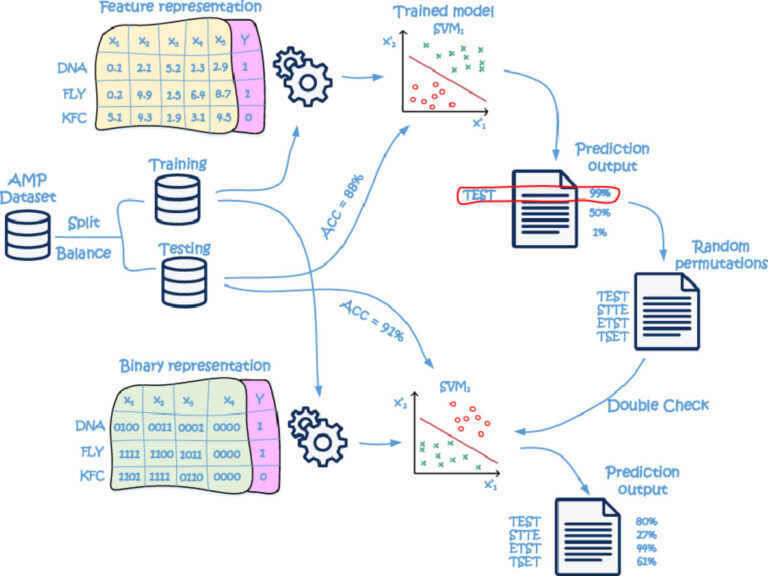
Applying Machine Learning for the Discovery of Peptides with Catalytic Activity
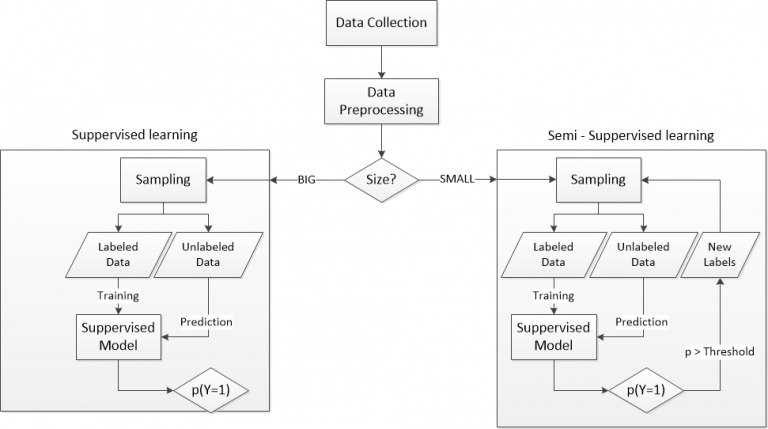
Institution: Faculty of Engineering, University of Rijeka Objective: The aim of this project proposal is to build a catalytic activity prediction model for peptides that would drive a smart exploration of huge chemical search space.
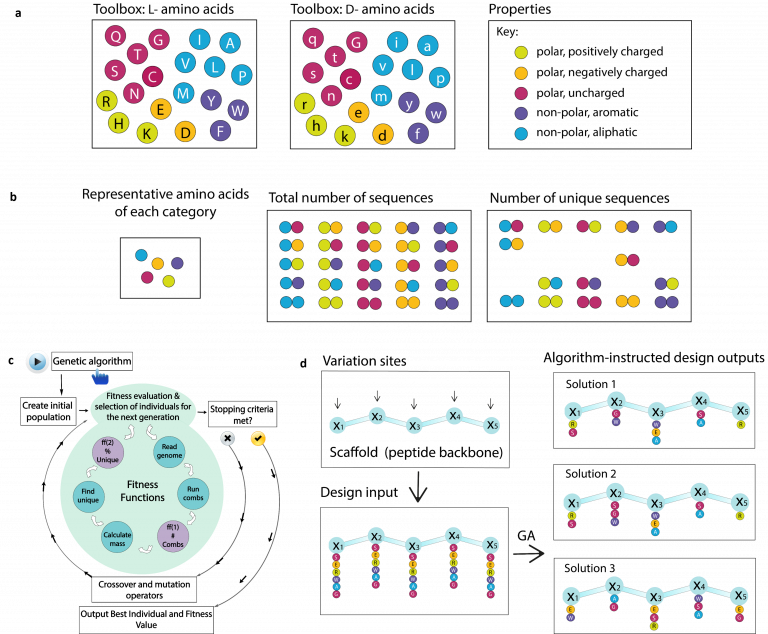
Algorithm-supported, mass and sequence diversity-oriented random peptide library design
Random peptide libraries that cover large search spaces are often used for the discovery of new binders, even when the target is unknown. To ensure an accurate population representation, there is a tendency to use large libraries. However, parameters such as the synthesis scale, the number of library members, the sequence deconvolution and peptide structure […]
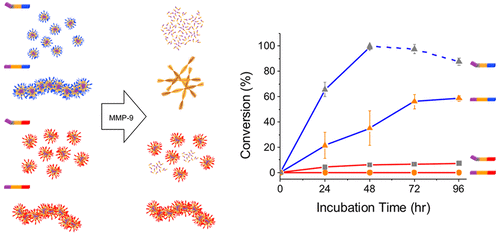
Customizing morphology, size, and response kinetics of matrix metalloproteinase-responsive nanostructures by systematic peptide design
Overexpression and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) is associated with multiple diseases and can serve as a stimulus to activate nanomaterials for sensing and controlled release. In order to achieve autonomous therapeutics with improved space-time targeting capabilities, several features need to be considered beyond the introduction of an enzyme-cleavable linker into a nanostructure. We introduce […]
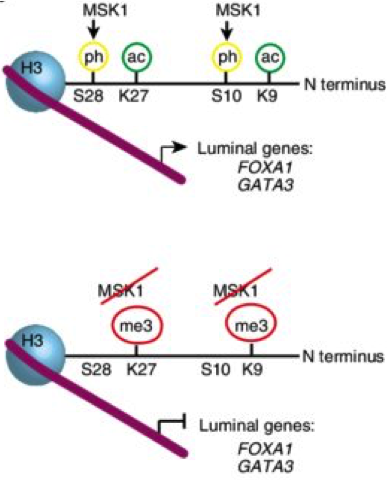
MSK1 regulates luminal cell differentiation and metastatic dormancy in ER+ breast cancer
For many patients with breast cancer, symptomatic bone metastases appear after years of latency. How micrometastatic lesions remain dormant and undetectable before initiating colonization is unclear. Here, we describe a mechanism involved in bone metastatic latency of oestrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer. Using an in vivo genome-wide short hairpin RNA screening, we identified the kinase […]
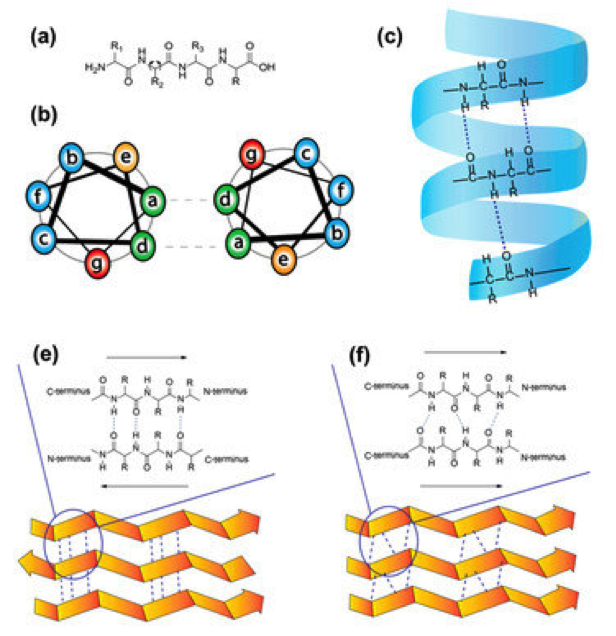
Cell-penetrating peptides: Design strategies beyond primary structure and amphipathicity
Efficient intracellular drug delivery and target specificity are often hampered by the presence of biological barriers. Thus, compounds that efficiently cross cell membranes are the key to improving the therapeutic value and on-target specificity of non-permeable drugs. The discovery of cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) and the early design approaches through mimicking the natural penetration domains used […]