The subject of this project is compound flooding in coastal areas due to high sea and river levels. Compound flooding is a global research priority due to the increasing occurrence in the context of climate change. The problem of compound flooding in coastal rivers is challenging because of a complex interaction between several factors, including […]
Laboratory for Hybrid Computational Methods
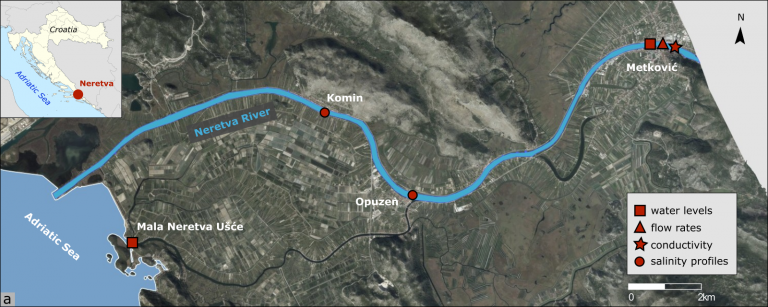
Estimating River Discharges in Highly Stratified Estuaries
Estuaries are transitional areas between river and marine environments. Understanding the estuarine dynamics is important for various water management issues, such as predicting floods and droughts, assessing impacts of sea level rise, planning freshwater intake for irrigation, and managing sediment transport. One of the key requirements for understanding and predicting the estuarine dynamics is to […]
Nino Krvavica held an interesting presentation on “Is There a Place for AI in Civil Engineering?”
Assit. prof. dr. sc. Nino Krvavica held an interesting presentation on “Is there a place for AI in civil engineering?” with the presentation of his recent scientific work and open problems in civil engineering which can be solved using ML.
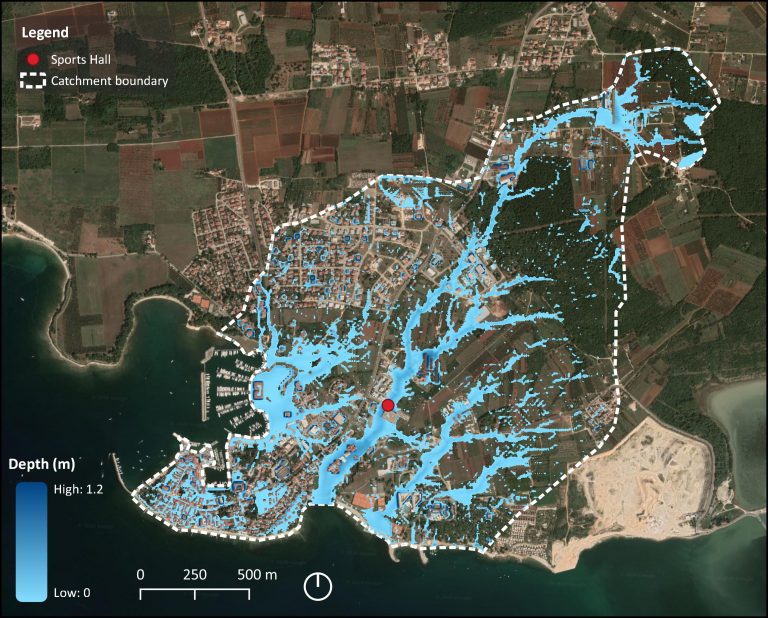
Evaluation of Design Storms and Critical Rainfall Durations for Flood Prediction in Partially Urbanized Catchments
This study investigates and compares several design storms for flood estimation in partially urbanized catchments. Six different design storms were considered: Euler II, Alternating Block Method, Average Variability Method, Huff’s curves, and uniform rainfall. Additionally, two extreme historical storms have been included for comparison. A small, ungauged, partially urbanized catchment in Novigrad (Croatia) was chosen […]
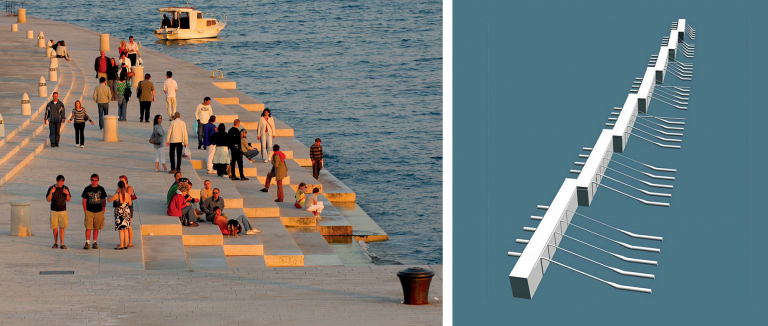
Time-dependent numerical model for simulating internal oscillations in a sea organ
This paper presents a one-dimensional time-dependent numerical model of a sea organ, which generates music driven by the motion of the sea. The governing equations are derived by coupling hydrodynamic and thermodynamic equations for water level and air pressure oscillations in a sea organ pipe system forced by irregular waves. The model was validated by […]
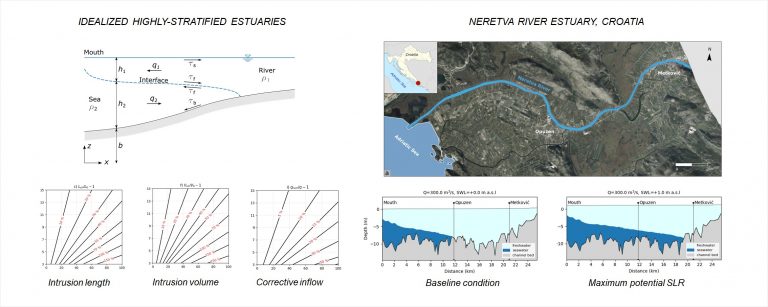
Assessment of sea-level rise impacts on salt-wedge intrusion in idealized and Neretva River Estuary
Understanding the response of estuaries to sea-level rise is crucial in developing a suitable mitigation and climate change adaptation strategy. This study investigates the impacts of rising sea levels on salinity intrusion in salt-wedge estuaries. The sea-level rise impacts are assessed in idealized estuaries using simple expressions derived from a two-layer hydraulic theory, and in […]
Nino Krvavica talks about his research for radio station Rijeka
Re-evaluating efficiency of first-order numerical schemes for two-layer shallow water systems by considering different eigenvalue solutions
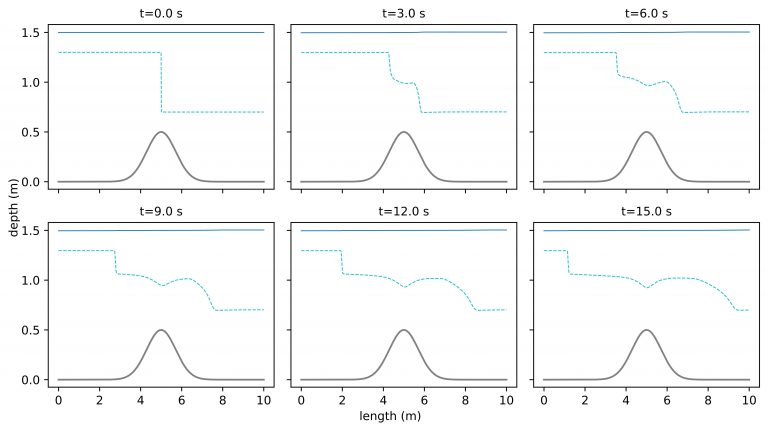
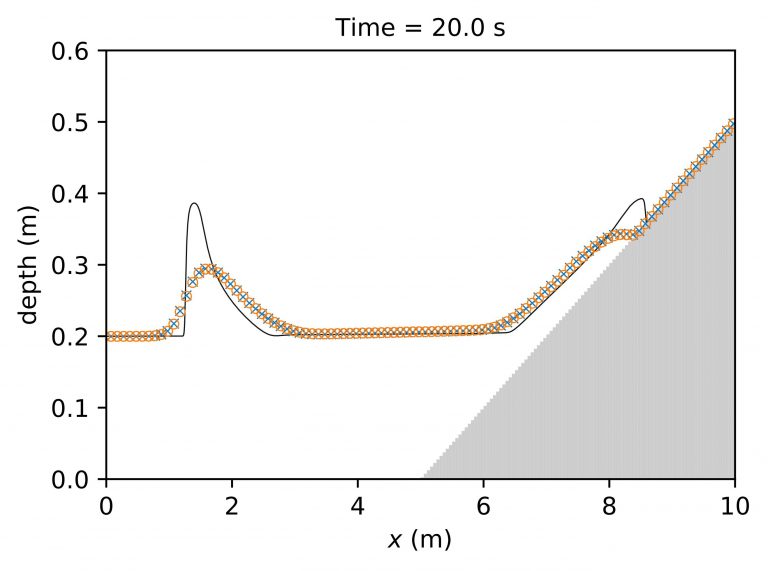
The efficiency of several first-order numerical schemes for two-layer shallow water equations (SWE) are evaluated here by considering different eigenvalue solutions. This study is a continuation of our previous work (Krvavica et al., 2018) in which we have proposed an efficient implementation of a Roe solver for two-layer SWE based on analytical expressions for eigenvalues […]
Sustainable Construction of Artificial Gravel Beaches – Construction of New Beaches and an Increase of Existing Capacity (BEACHEX)
A scientific project conducted by the Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Zagreb with the Lancaster Environment Centre, Lancaster University that has been fully supported by the “Research Cooperability“ Program of the Croatian Science Foundation funded by the European Union from the European Social Fund under the Operational Programme Efficient Human Resources 2014-2020.
Analytical implementation of Roe solver for two-layer shallow water equations with accurate treatment for loss of hyperbolicity
A new implementation of the Roe scheme for solving two-layer shallow-water equations is presented in this paper. The proposed A-Roe scheme is based on the analytical solution to the characteristic quartic of the flux matrix, which is an efficient alternative to a numerical eigensolver. Additionally, an accurate method for maintaining the hyperbolic character of the governing system […]