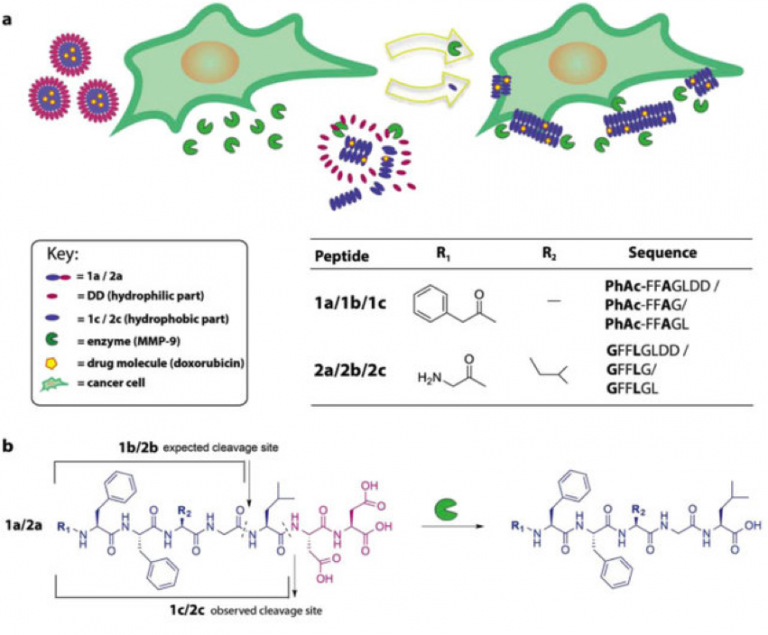
A central challenge in cancer care is to ensure that therapeutic compounds reach their targets. One approach is to use enzyme-responsive biomaterials, which reconfigure in response to endogenous enzymes that are overexpressed in diseased tissues, as potential site-specific anti-tumoral therapies. Here we report peptide micelles that upon MMP-9 catalyzed hydrolysis reconfigure to form fibrillar nanostructures. […]
Laboratory for Drug Design
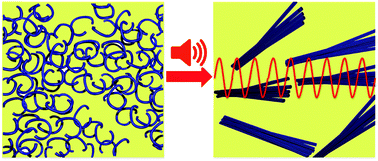
Alignment of nanostructured tripeptide gels by directional ultrasonication
We demonstrate an in situ ultrasonic approach to influence self-assembly across the supramolecular to micron length scales, showing enhancement of supramolecular interactions, chirality and orientation, which depends on the peptide sequence and solvent environment. This is the first successful demonstration of using oscillating pressure waves to generate anisotropic organo- and hydrogels consisting of oriented tripeptides structures.
Exploring the sequence space for (tri-)peptide self-assembly to design and discover new hydrogels
Peptides that self-assemble into nanostructures are of tremendous interest for biological, medical, photonic and nanotechnological applications. The enormous sequence space that is available from 20 amino acids probably harbours many interesting candidates, but it is currently not possible to predict supramolecular behaviour from sequence alone. Here, we demonstrate computational tools to screen for the aqueous […]
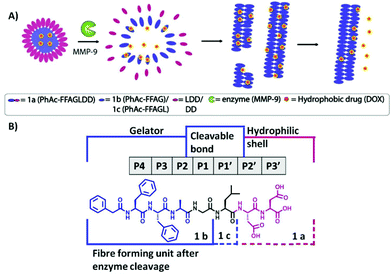
MMP-9 triggered micelle-to-fibre transitions for slow release of doxorubicin
Phenylacetyl-peptide amphiphiles were designed, which upon cleavage by a disease-associated enzyme reconfigure from micellar aggregates to fibres. Upon this morphological change, a doxorubicin payload could be retained in the fibres formed, which makes them valuable carriers for localised formation of nanofibre depots for slow release of hydrophobic anticancer drugs.