Invited talk on “Local Entropy Measures with Applications in Biomedicine” by Assis. Prof. Jonatan Lerga, PhD, at the 7th Conference on Information Theory and Complex Systems (TINKOS 2019), Belgrade, Serbia, was held on the 15th of October, 2019.
News
A Study on Cyber Security Threats in a Shipboard Integrated Navigational System
The integrated navigational system (INS) enhances the effectiveness and safety of ship navigation by providing multifunctional display on the basis of integration of at least two navigational functions, the voyage route monitoring with Electronic Chart Display and Information System (ECDIS) and collision avoidance with radar. The INS is essentially a software platform for fusion of […]
Visiting Professor Lecture: László Szabó form the Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, Hungary
Prof. László Szabó (Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, Hungary) held an interesting lecture on the stable matching problem at the Faculty of Engineering on 3rd of October, 2019. The event took place at the Faculty of Engineering, University of Rijeka (www.riteh.uniri.hr).
SKILLSEA
Technology and digitalisation are transforming the shipping industry. ‘Smart’ ships are coming into service, creating demand for a new generation of competent, highly-skilled maritime professionals. Europe is a traditional global source of maritime expertise and the four-year SKILLSEA project is launched with the aim of ensuring that the region’s maritime professionals possess key digital, green […]
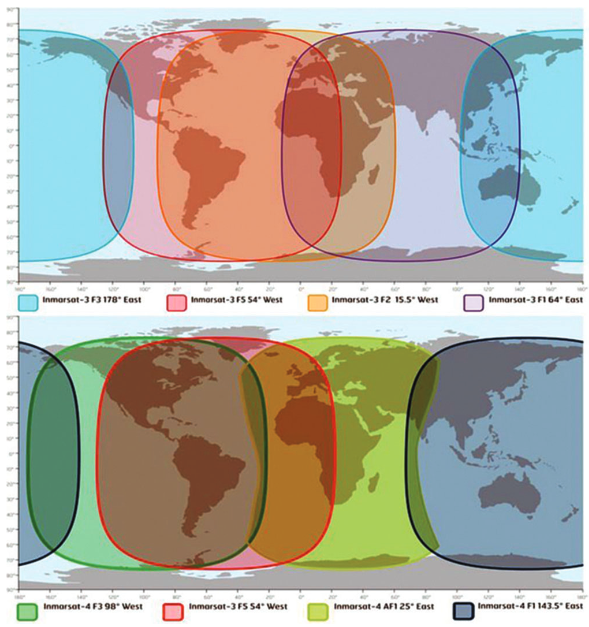
An Overview of Recent Changes in the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System Regarding Maritime Mobile Satellite Service
For a long time, Inmarsat satellite system was the only maritime mobile satellite service provider when Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) is concerned. This satellite system has different generations of its satellites providing a wide range of services and applications. In 2018, its services related to the GMDSS have migrated to a newer […]
Organized Congress “2nd Conference on Machine Learning for Gravitational Waves, Geophysics and Control Systems”
A congress “2nd Conference on Machine Learning for Gravitational Waves, Geophysics and Control Systems” was organized at the Faculty of Engineering with the participation of some of the leading scientists in the fields of physics, signal processing, and artificial intelligence from 20 countries. The conference was organized at the Faculty of Engineering, University of Rijeka […]
Multi3Generation: Multi-task, Multilingual, Multi-modal Language Generation
Language generation (LG) is a crucial technology if machines are to communicate with humans seamlessly using human natural language. A great number of different tasks within Natural Language Processing (NLP) are language generation tasks, and being able to effectively perform these tasks implies (1) that machines are equipped with world knowledge that can require multi-modal […]
Maritime Cyber Risk Management: An Experimental Ship Assessment
The maritime transport industry is increasingly reliant on computing and communication technologies, and the need for cyber risk management of critical systems and assets on vessels is becoming critically important. In this paper, a comprehensive cyber risk assessment of a ship is presented. An experimental process consisting of assessment preparation activities, assess- ment conduct and […]
Language guidance tool for improving language knowledge
In line with EU language policy and its efforts to promote mobility and intercultural understanding, language acquisition and multilingualism represent important elements of the EU’s language policy, promoting the knowledge of 2 languages in addition to the mother tongue. In line with the linguistic background of the EU policy the project “LanGuide” is focused on […]
Invited talk at SSIP 2019
Ivan Štajduhar gave a lecture titled “Everything you never wanted to know about machine learning, but were forced to find out” at the 2019 Summer School on Image Processing (SSIP) in Timisoara, Romania, on July 10, 2019. https://www.info.uvt.ro/ssip2019/