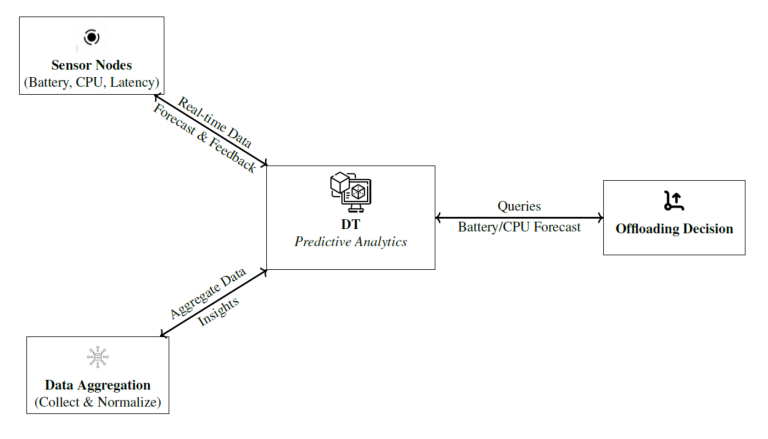
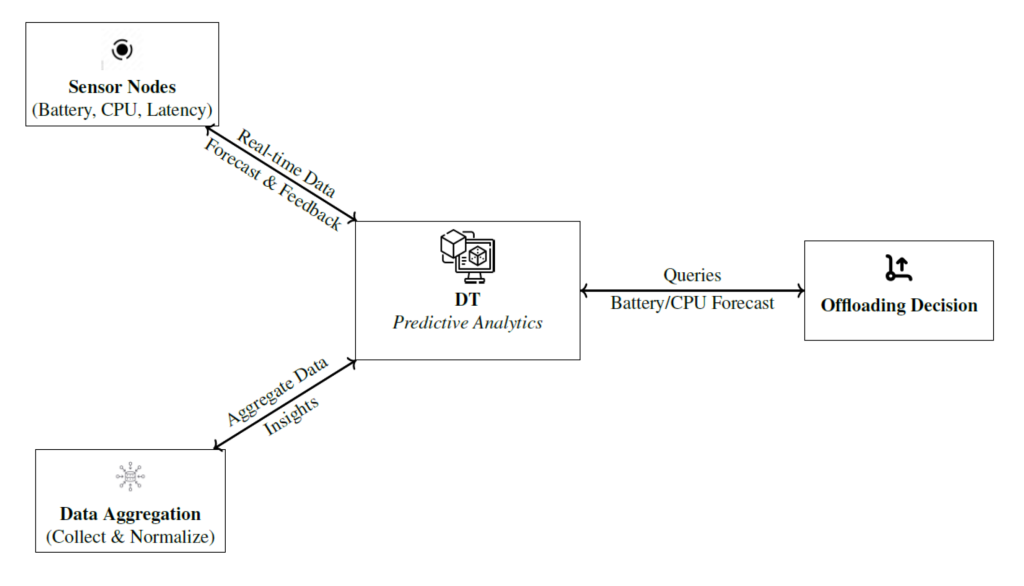
Effectively managing the vast data generated by sensor networks has become crucial with the rapid spread of IoT devices under strict resource constraints. This research introduces a framework that integrates explainable artificial intelligence (XAI), digital twins (DT), federated learning (FL), and multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) to optimise energy use and task distribution in distributed IoT environments. The proposed method, called explainable digital twin with federated multi-agent RL (XDT-FMARL), balances computational load through federated training and intelligent offloading between constrained IoT devices and edge servers. DT predicts short-term operational metrics such as battery state, processor load, and network delay using linear regression and moving averages. Guided by XAI, MARL agents select adaptive offloading or local processing strategies, enhancing interpretability and trust. Experiments show that XDT-FMARL maintains device batteries above 80% and applies responsive offloading under high load, while single-agent models default to uniform local processing with limited adaptability.