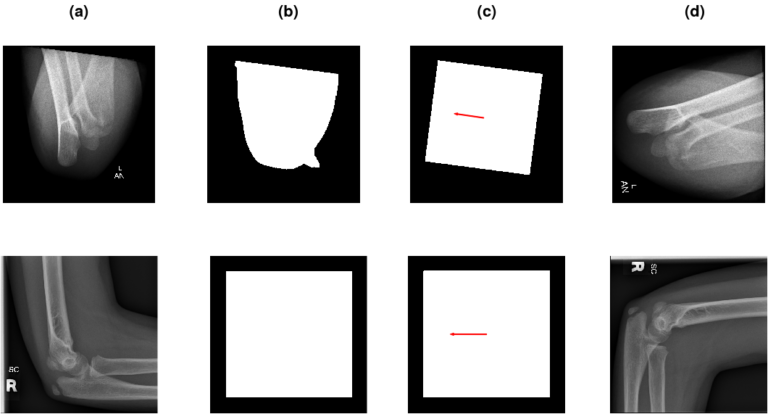
Background and objectives: Computer-aided diagnosis relies on machine learning algorithms that require filtered and preprocessed data as the input. Aligning the image in the desired direction is an additional manual step in post- processing, commonly overlooked due to workload issues. Several state-of-the-art approaches for fracture detection and disease-struck region segmentation benefit from correctly oriented images, thus requiring such preprocessing of X-ray images. Furthermore, it is desirable to have archived studies in a standardized format. Radiograph hanging protocols also differ from case to case, which means that images are not always aligned and oriented correctly. As a solution, the paper proposes XAOM, an X-ray Alignment and Orientation Method for images from 21 different body regions.
Methods: Typically, other methods are crafted for this purpose to suit a specific body region and form of usage. In contrast, the method proposed in this paper is comprehensive and easily tuned to align and orient X- ray images of any body region. XAOM consists of two stages. For the first stage of the method, aligning X-ray images, we experimented with the following approaches: Hough transform, Fast line detection algorithm, and Principal Component Analysis method. For the second stage, we have experimented with the adaptations of several well known convolutional neural network topologies for correctly predicting image orientation: LeNet5, AlexNet, VGG16, VGG19, and ResNet50.
Results: In the first stage, the PCA-based approach performed best. The average difference between the angle detected by the algorithm and the angle marked by the experts on the test set containing 200 pediatric X-ray images was 1.65°, while the median value was 0.11°. In the second stage, the VGG16-based network topology achieved the best accuracy of 0.993 on a test set containing 4, 221 images. Conclusion XAOM is highly accurate at aligning and orienting pediatric X-ray images of 21 common body regions according to a set standard. The proposed method is also robust and can be easily adjusted to the different alignment and rotation criteria.
Availability: The Python source code of the best performing implementation of XAOM is publicly available at https://github.com/fhrzic/XAOM.