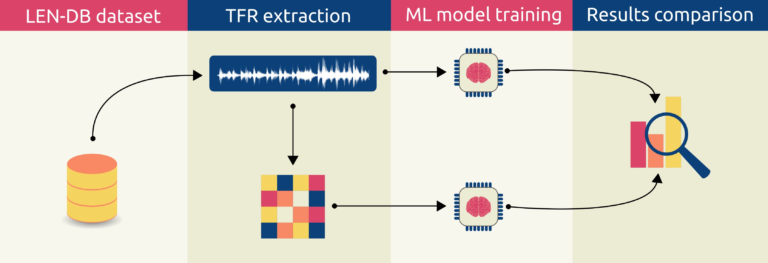
Non-stationary signals are often analyzed using raw waveform data or spectrograms of those data; however, the possibility of alternative time–frequency representations being more informative than the original data or spectrograms is yet to be investigated. This paper tested whether alternative time–frequency representations could be more informative for machine learning classification of seismological data. The mentioned hypothesis was evaluated by training three well-established convolutional neural networks using nine time–frequency representations. The results were compared to the base model, which was trained on the raw waveform data. The signals that were used in the experiment are three-component seismogram instances from the Local Earthquakes and Noise DataBase (LEN-DB). The results demonstrate that Pseudo Wigner–Ville and Wigner–Ville time–frequency representations yield significantly better results than the base model, while spectrogram and Margenau–Hill perform significantly worse (p < 0.01). Interestingly, the spectrogram, which is often used in signal analysis, had inferior performance when compared to the base model. The findings presented in this research could have notable impacts in the fields of geophysics and seismology as the phenomena that were previously hidden in the seismic noise are now more easily identified. Furthermore, the results indicate that applying Pseudo Wigner–Ville or Wigner–Ville time–frequency representations could result in a large increase in earthquakes in the catalogs and lessen the need to add new stations with an overall reduction in the costs. Finally, the proposed approach of extracting valuable information through time–frequency representations could be applied in other domains as well, such as electroencephalogram and electrocardiogram signal analysis, speech recognition, gravitational waves investigation, and so on.