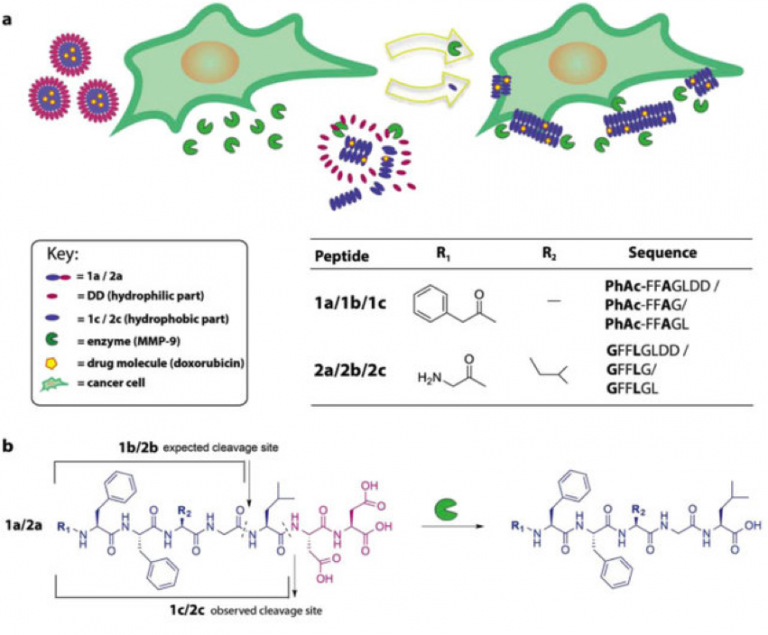
A central challenge in cancer care is to ensure that therapeutic compounds reach their targets. One approach is to use enzyme-responsive biomaterials, which reconfigure in response to endogenous enzymes that are overexpressed in diseased tissues, as potential site-specific anti-tumoral therapies. Here we report peptide micelles that upon MMP-9 catalyzed hydrolysis reconfigure to form fibrillar nanostructures. These structures slowly release a doxorubicin payload at the site of action. Using both in vitro and in vivo models, we demonstrate that the fibrillar depots are formed at the sites of MMP-9 overexpression giving rise to enhanced efficacy of doxorubicin, resulting in inhibition of tumor growth in an animal model.