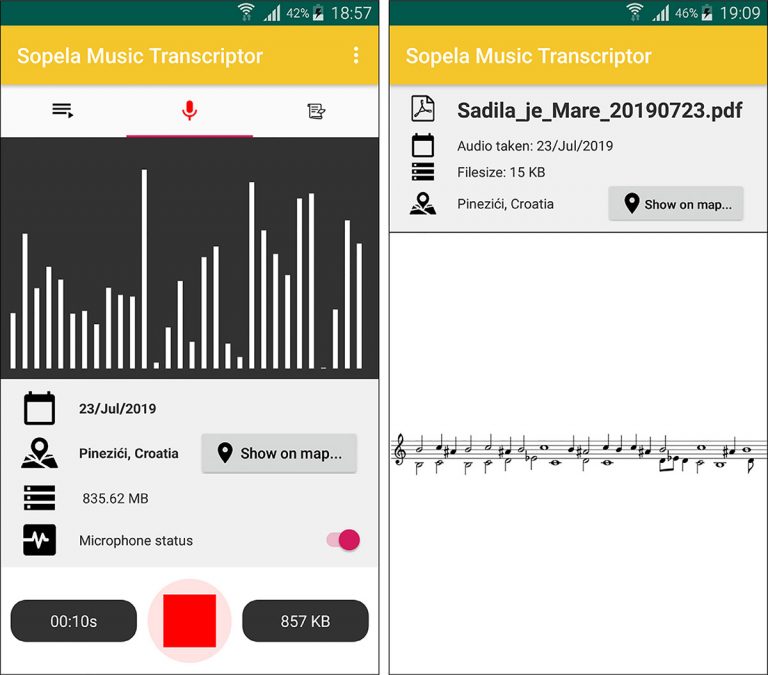
Sopela is a traditional hand-made woodwind instrument, commonly played in pair, characteristic to the Istrian peninsula in western Croatia. Its piercing sound, accompanied by two-part singing in the hexatonic Istrian scale, is registered in the UNESCO Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity. This paper presents an insight study of automatic music transcription (AMT) for sopele tunes. The process of converting audio inputs into human-readable musical scores involves multi-pitch detection and note tracking. The proposed solution supports this process by utilising frequency-feature extraction, supervised machine learning (ML) algorithms, and postprocessing heuristics. We determined the most favourable tone-predicting model by applying grid search for two state-of-the-art ML techniques, optionally coupled with frequency-feature extraction. The model achieved promising transcription accuracy for both monophonic and polyphonic music sources encompassed in the originally developed dataset. In addition, we developed a proof-of-concept AMT system, comprised of a client mobile application and a server-side API. While the mobile application records, tags and uploads audio sources, the back-end server applies the presented procedure for converting recorded music into a common notation to be delivered as a transcription result. We thus demonstrate how collecting and preserving traditional sopele music, performed in real-life occasions, can be effortlessly accomplished on-the-go.
The research was conducted at the Faculty of Engineering, University of Rijeka (www.riteh.uniri.hr).