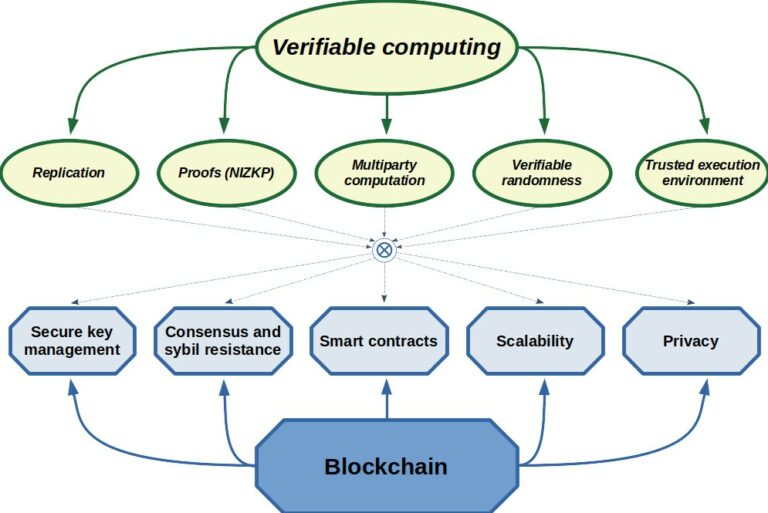
Verifiable computing applications for sustainable and scalable public blockchains.
Context and motivation
A public blockchain is a distributed, decentralized, and shared ledger that requires no central authority and eliminates the need for third-party verification. It was first introduced for the Bitcoin cryptocurrency as a public ledger to record all transactions. It provides trust when the parties involved do not trust each other. Instead of trusting an authority or intermediary, trust is transferred to a computer code. This code runs on computers called nodes that are connected in a peer-to-peer (P2P) network. The need for an intermediary is avoided by using a distributed, cryptographically secured ledger that everyone agrees to. The ledger can only be updated by consensus between all parties involved. In order to participate in consensus, where identities can be anonymous, and in the presence of malicious nodes that do not follow the rules, a sybil-resistance mechanism must be in place. One such mechanism is Proof-of-Work (PoW) where participants must perform some computational work to validate new data with all other participants before it can be appended to the blockchain. In PoW, network participants (called miners) typically perform cryptographic computations to solve puzzles and get the right to update the ledger and get the corresponding reward. The competition for the reward requires increasing amounts of effort to solve the puzzles thus preventing anyone that lacks resources to carry out the attack. The high energy consumption of the PoW consensus protocol and limited transaction throughput motivate the development of alternative mechanisms such as Proof-of-Useful-Work (PoUW) which focuses on solving practical problems instead of cryptographic puzzles, and Proof-of-Stake (PoS), which uses stake in the blockchain, i.e. cryptocurrency supporting the blockchain network, as voting power.
Project goal
Verifiable computing is a new and interesting research area that addresses the need to efficiently verify the results of computations delegated to untrusted third parties. In an effort to find a sustainable replacement for Proof-of-Work, this project explores solutions that use verifiable computing techniques to verify work in a Proof-of-Useful-Work consensus mechanism without relying on a trusted execution environment.
